Test Yourself
Q1: Multiple Choice Type:
i. Each interior angle of a regular polygon is 165°. The number of sides in the polygon is:
Step 1: Let the number of sides be \( n \).
Each interior angle \( = 165^\circ \).
Each exterior angle \( = 180^\circ – 165^\circ = 15^\circ \).
Number of sides:
\[
n = \frac{360^\circ}{15^\circ} = 24
\]Answer: b. 24
ii. Two angles of a quadrilateral are 50° each and the other two angles are equal. The measure of each of these equal angles is:
Step 1: Sum of interior angles of quadrilateral = \(360^\circ\).
Given two angles = 50° and 50°, let each equal angle be \( x \).
\[
50^\circ + 50^\circ + x + x = 360^\circ \\
100^\circ + 2x = 360^\circ \Rightarrow 2x = 260^\circ \Rightarrow x = 130^\circ
\]Answer: a. 130°
iii. A polygon has \( n \) sides, the number of diagonals in this polygon is:
Number of diagonals of an \( n \)-sided polygon is:
\[
\frac{n(n – 3)}{2}
\]Answer: c. \(\frac{1}{2} \times n (n – 3)\)
iv. The interior angle of a regular polygon is four times its exterior angle. The number of sides in the polygon is:
Let exterior angle = \( x \), interior angle = \( 4x \).
Since supplementary:
\[
x + 4x = 180^\circ \Rightarrow 5x = 180^\circ \Rightarrow x = 36^\circ
\]
Number of sides:
\[
n = \frac{360^\circ}{36^\circ} = 10
\]Answer: b. 10
v. Two angles of a quadrilateral are 69° and 113°. If the other two angles are equal then each of equal angles is:
Sum of interior angles = \(360^\circ\).
Let each equal angle be \( x \).
\[
69^\circ + 113^\circ + x + x = 360^\circ \\
182^\circ + 2x = 360^\circ \Rightarrow 2x = 178^\circ \Rightarrow x = 89^\circ
\]Answer: a. 89°
vi. Statement 1: A polygon whose one or more interior angle is less than two right angles is called a convex polygon.
Statement 2: The line joining any two consecutive vertices of a triangle of a polygon is called its diagonal.
Which of the following options is correct?
Explanation: – Statement 1 is false because a convex polygon is one where all interior angles are less than 180° (two right angles). If one or more interior angles are greater than 180°, the polygon is concave.
– Statement 2 is false because a diagonal joins two non-consecutive vertices, not consecutive vertices.
Answer: b. Both the statements are false.
vii. Assertion (A): It is possible to have a regular polygon, the sum of whose interior angles is 1000°.
Reason (R): The sum of the interior angles of a polygon with \( n \) sides = \( (2n – 4) \times 90^\circ \).
Explanation: – The correct formula for the sum of interior angles of a polygon is:
\[
(n – 2) \times 180^\circ
\]
– The formula given in Reason (R) is incorrect.
– To check if sum = 1000° is possible:
\[
(n – 2) \times 180^\circ = 1000^\circ \Rightarrow n – 2 = \frac{1000}{180} \approx 5.56
\]
– \( n \) is not an integer, so a regular polygon with sum 1000° does not exist.
Answer: d. A is false, but R is true.
viii. Assertion (A): The sum of interior angles of a regular polygon is thrice the sum of its exterior angles. The polygon is an octagon.
Reason (R): Each interior angle of a regular polygon = \( \frac{(n – 2) \times 180^\circ}{n} \).
Step 1: Evaluate Assertion (A).
The sum of exterior angles of any polygon is always 360°.
According to the assertion, Sum of interior angles = 3 360° = 1080°.
Using the formula for sum of interior angles: (n – 2) 180° = 1080°.
(n – 2) = 1080 / 180 = 6.
n = 6 + 2 = 8.
A polygon with 8 sides is an octagon. So, Assertion (A) is true.
Step 2: Evaluate Reason (R).
The formula for each interior angle of a regular polygon is indeed ((n – 2) 180°) / n.
So, Reason (R) is true.
Step 3: Determine the relationship.
While both statements are true, the assertion about the sum of angles is proven using the sum formula ((n – 2) 180°), not the individual angle formula given in the reason.
Therefore, R is not the direct explanation for A.
Answer: b. Both A and R are correct, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
ix. Assertion (A): The number of diagonals of a nonagon = 27
Reason (R): The number of diagonals of an n-sided polygon = \( \frac{n(n-1)}{2} – n \).
Step 1: Evaluate Reason (R).
The formula for the number of diagonals in an n-sided polygon is:
Diagonals = [n(n-3)] / 2
This is algebraically identical to: [n(n-1)/2] – n
Let’s check: (n² – n)/2 – 2n/2 = (n² – 3n)/2 = n(n-3)/2
So, Reason (R) is true.
Step 2: Evaluate Assertion (A) using the formula from R.
A nonagon has n = 9 sides.
Number of diagonals = [9(9-1)/2] – 9
Number of diagonals = [9 8 / 2] – 9
Number of diagonals = [72 / 2] – 9
Number of diagonals = 36 – 9 = 27
So, Assertion (A) is true.
Step 3: Determine the relationship.
Since the formula provided in Reason (R) was used to correctly calculate the value in Assertion (A), R is the correct explanation for A.
Answer: a. Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation for A.
x. Assertion (A): The ratio between the exterior and interior angle of a regular polygon is 1 : 8. The number of sides of the regular polygon is 18.
Reason (R): The sum of the exterior angles and interior angles of a convex polygon are 360° and \( 2(n – 1) \times 90^\circ \) respectively.
Explanation: – Given ratio:
\[
\frac{\text{exterior angle}}{\text{interior angle}} = \frac{1}{8}
\]
– Let exterior angle = \( x \), interior angle = \( 8x \).
– Interior + exterior = 180°:
\[
x + 8x = 180^\circ \Rightarrow 9x = 180^\circ \Rightarrow x = 20^\circ
\]
– Number of sides:
\[
n = \frac{360^\circ}{x} = \frac{360^\circ}{20^\circ} = 18
\]
– Reason (R) formula for interior angle sum is incorrect.
Answer: c. A is true, but R is false.
Q2: The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 7. If the difference between the largest and the smallest of these angles is 76°, find the fourth angle of the quadrilateral.
Step 1: Let the angles be \(3x\), \(5x\), and \(7x\).
Step 2: Given that the difference between the largest and smallest angle is 76°:
\[
7x – 3x = 76^\circ \\
4x = 76^\circ \Rightarrow x = \frac{76}{4} = 19^\circ
\]Step 3: Calculate the three known angles:
\[
3x = 3 \times 19^\circ = 57^\circ \\
5x = 5 \times 19^\circ = 95^\circ \\
7x = 7 \times 19^\circ = 133^\circ
\]Step 4: Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral = 360°.
Let the fourth angle be \( y \). Then:
\[
57^\circ + 95^\circ + 133^\circ + y = 360^\circ \\
285^\circ + y = 360^\circ \Rightarrow y = 360^\circ – 285^\circ = 75^\circ
\]Answer: The fourth angle of the quadrilateral is 75°.
Q3: Three angles of a quadrilateral are in ratio 4 : 5 : 6. The sum of the least and the greatest of these angles is 160°. Find all the angles of the quadrilateral.
Step 1: Let the three angles be \(4x\), \(5x\), and \(6x\).
Step 2: Given that the sum of the least and greatest angles is 160°:
\[
4x + 6x = 160^\circ \\
10x = 160^\circ \Rightarrow x = \frac{160}{10} = 16^\circ
\]Step 3: Calculate the three angles:
\[
4x = 4 \times 16^\circ = 64^\circ \\
5x = 5 \times 16^\circ = 80^\circ \\
6x = 6 \times 16^\circ = 96^\circ
\]Step 4: Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
Let the fourth angle be \( y \). Then:
\[
64^\circ + 80^\circ + 96^\circ + y = 360^\circ \\
240^\circ + y = 360^\circ \Rightarrow y = 360^\circ – 240^\circ = 120^\circ
\]Answer: The four angles of the quadrilateral are 64°, 80°, 96°, and 120°.
Q4: The sum of three angles of a quadrilateral is 5 times the fourth angle. Find the fourth angle.
Step 1: Let the fourth angle be \( x^\circ \).
Step 2: Given, sum of the other three angles is \( 5x \).
Step 3: Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral = 360°:
\[
x + 5x = 360^\circ \\
6x = 360^\circ \Rightarrow x = \frac{360^\circ}{6} = 60^\circ
\]Answer: The fourth angle is 60°.
Q5: A heptagon has four angles each of 132° and the remaining three angles are equal. Find the size of each of the three equal angles.
Step 1: Number of sides in heptagon \( n = 7 \).
Step 2: Sum of interior angles of a polygon is:
\[
(n – 2) \times 180^\circ = (7 – 2) \times 180^\circ = 5 \times 180^\circ = 900^\circ
\]Step 3: Sum of four given angles:
\[
4 \times 132^\circ = 528^\circ
\]Step 4: Let each of the remaining three equal angles be \( x^\circ \). Then:
\[
528^\circ + 3x = 900^\circ \\
3x = 900^\circ – 528^\circ = 372^\circ \\
x = \frac{372^\circ}{3} = 124^\circ
\]Answer: Each of the three equal angles is 124°.
Q6: Each interior angle of a regular polygon is 144°. Find the interior angle of a regular polygon which has double the number of sides as the first polygon.
Step 1: Let the number of sides of the first polygon be \( n \).
Each interior angle \( = 144^\circ \).
Step 2: Find the number of sides \( n \):
Each exterior angle \( = 180^\circ – 144^\circ = 36^\circ \).
\[
n = \frac{360^\circ}{36^\circ} = 10
\]Step 3: The second polygon has double the number of sides:
\[
2n = 2 \times 10 = 20
\]Step 4: Find the interior angle of the second polygon:
Each exterior angle \( = \frac{360^\circ}{20} = 18^\circ \).
Each interior angle \( = 180^\circ – 18^\circ = 162^\circ \).
Answer: The interior angle of the second polygon is 162°.
Q7: The exterior angles of a pentagon are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3 : 4 : 5. Find its interior angles.
Step 1: Let the exterior angles be \( x \), \( 2x \), \( 3x \), \( 4x \), and \( 5x \).
Step 2: Sum of exterior angles of any polygon is \( 360^\circ \):
\[
x + 2x + 3x + 4x + 5x = 360^\circ \\
15x = 360^\circ \Rightarrow x = \frac{360^\circ}{15} = 24^\circ
\]Step 3: Calculate each exterior angle:
\[
x = 24^\circ, \quad 2x = 48^\circ, \quad 3x = 72^\circ, \quad 4x = 96^\circ, \quad 5x = 120^\circ
\]Step 4: Find each interior angle (interior angle \( = 180^\circ – \) exterior angle):
\[
180^\circ – 24^\circ = 156^\circ \\
180^\circ – 48^\circ = 132^\circ \\
180^\circ – 72^\circ = 108^\circ \\
180^\circ – 96^\circ = 84^\circ \\
180^\circ – 120^\circ = 60^\circ
\]Answer: The interior angles of the pentagon are 156°, 132°, 108°, 84°, and 60°.
Q8: The angles of a pentagon are \( x^\circ \), \( (x – 10)^\circ \), \( (x + 20)^\circ \), \( (2x + 44)^\circ \), and \( (2x – 70)^\circ \). Find the value of \( x \).
Step 1: Find the sum of the interior angles of a pentagon.
Formula: Sum of angles = (n – 2) 180°
Here, n = 5 (for a pentagon)
Sum = (5 – 2) 180°
Sum = 3 180° = 540°
Step 2: Form an equation by adding all the given angles.
x + (x – 10) + (x + 20) + (2x – 44) + (2x – 70) = 540
Step 3: Simplify the equation by combining like terms.
(x + x + x + 2x + 2x) + (-10 + 20 – 44 – 70) = 540
7x – 104 = 540
Step 4: Solve for the value of x.
7x = 540 + 104
7x = 644
x = 644 / 7
x = 92
Answer: The value of x is 92.
Q9: In quadrilateral ABCD, sides AB and DC are parallel. If \( \angle A : \angle D = 2 : 3 \) and \( \angle B : \angle C = 7 : 8 \), find all the angles of quadrilateral ABCD.
Step 1: Understand the property of parallel sides.
Since AB || DC, the quadrilateral is a trapezium.
In a trapezium with parallel sides AB and DC, the sum of co-interior angles is 180°.
Therefore, ∠A + ∠D = 180° and ∠B + ∠C = 180°.
Step 2: Solve for ∠A and ∠D.
Given ratio ∠A : ∠D = 2 : 3
Let ∠A = 2x and ∠D = 3x
2x + 3x = 180°
5x = 180°
x = 180° / 5 = 36°
∠A = 2 36° = 72°
∠D = 3 36° = 108°
Step 3: Solve for ∠B and ∠C.
Given ratio ∠B : ∠C = 7 : 8
Let ∠B = 7y and ∠C = 8y
7y + 8y = 180°
15y = 180°
y = 180° / 15 = 12°
∠B = 7 12° = 84°
∠C = 8 12° = 96°
Step 4: Verify the total sum of angles.
Sum = ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D
Sum = 72° + 84° + 96° + 108° = 360°
(The sum of interior angles of any quadrilateral is always 360°)
Answer: The angles are ∠A = 72°, ∠B = 84°, ∠C = 96°, and ∠D = 108°.
Q10: In quadrilateral ABCD; 2∠A = 3∠B = 2∠C = 6∠D. Find all the angles of quadrilateral ABCD.
Step 1: Let the common value be \( k \). Then:
\[
2\angle A = k \Rightarrow \angle A = \frac{k}{2} \\
3\angle B = k \Rightarrow \angle B = \frac{k}{3} \\
2\angle C = k \Rightarrow \angle C = \frac{k}{2} \\
6\angle D = k \Rightarrow \angle D = \frac{k}{6}
\]Step 2: Sum of all interior angles of a quadrilateral = 360°:
\[
\angle A + \angle B + \angle C + \angle D = 360^\circ
\]
Substitute the values:
\[
\frac{k}{2} + \frac{k}{3} + \frac{k}{2} + \frac{k}{6} = 360^\circ
\]Step 3: Find common denominator (6):
\[
\frac{3k}{6} + \frac{2k}{6} + \frac{3k}{6} + \frac{k}{6} = 360^\circ \\
\frac{3k + 2k + 3k + k}{6} = 360^\circ \\
\frac{9k}{6} = 360^\circ \\
\frac{3k}{2} = 360^\circ \Rightarrow 3k = 720^\circ \Rightarrow k = 240^\circ
\]Step 4: Calculate each angle:
\[
\angle A = \frac{240^\circ}{2} = 120^\circ \\
\angle B = \frac{240^\circ}{3} = 80^\circ \\
\angle C = \frac{240^\circ}{2} = 120^\circ \\
\angle D = \frac{240^\circ}{6} = 40^\circ
\]Answer: The angles of quadrilateral ABCD are 120°, 80°, 120°, and 40°.
Q11: The sum of interior angles of a regular polygon is thrice the sum of its exterior angles. Find the number of sides in the polygon.
Step 1: Sum of exterior angles of any polygon is:
\[
360^\circ
\]Step 2: Given sum of interior angles is thrice the sum of exterior angles:
\[
\text{Sum of interior angles} = 3 \times \text{Sum of exterior angles} = 3 \times 360^\circ = 1080^\circ
\]Step 3: Sum of interior angles of a polygon with \( n \) sides:
\[
(n – 2) \times 180^\circ = 1080^\circ
\]Step 4: Solve for \( n \):
\[
(n – 2) \times 180^\circ = 1080^\circ \\
n – 2 = \frac{1080^\circ}{180^\circ} = 6 \\
n = 6 + 2 = 8
\]Answer: The polygon has 8 sides.
Q12: Angles of a quadrilateral are (4x)°, 5(x+2)°, (7x-20)° and 6(x+3)°. Find:
i. The value of x
Step 1: Sum of all interior angles of a quadrilateral is:
\[
360^\circ
\]Step 2: Write the equation summing all angles:
\[
4x + 5(x+2) + (7x – 20) + 6(x+3) = 360
\]Step 3: Expand and simplify:
\[
4x + 5x + 10 + 7x – 20 + 6x + 18 = 360 \\
(4x + 5x + 7x + 6x) + (10 – 20 + 18) = 360 \\
22x + 8 = 360
\]Step 4: Solve for \(x\):
\[
22x = 360 – 8 = 352 \\
x = \frac{352}{22} = 16
\]Answer: \( x = 16 \)
ii. Each angle of the quadrilateral.
Step 5: Calculate each angle:
\[
4x = 4 \times 16 = 64^\circ \\
5(x+2) = 5 \times (16 + 2) = 5 \times 18 = 90^\circ \\
7x – 20 = 7 \times 16 – 20 = 112 – 20 = 92^\circ \\
6(x+3) = 6 \times (16 + 3) = 6 \times 19 = 114^\circ
\]Answer: The angles of the quadrilateral are 64°, 90°, 92°, and 114°.
Q13: Use the information given in the figure to find:
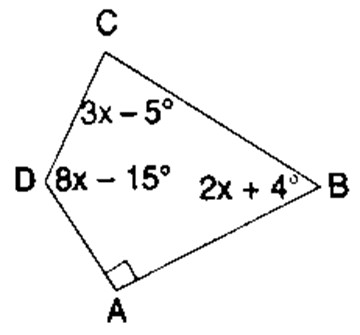
i. x
Step 1: From the figure, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
Angle at A is a right angle.
\[
\angle A = 90^\circ
\]Step 2: Given angles of the quadrilateral are:
\[
\angle B = (2x + 4)^\circ \\
\angle C = (3x – 5)^\circ \\
\angle D = (8x – 15)^\circ
\]Step 3: Sum of interior angles of a quadrilateral is:
\[
360^\circ
\]So,
\[
\angle A + \angle B + \angle C + \angle D = 360^\circ
\]Step 4: Substitute the given values:
\[
90 + (2x + 4) + (3x – 5) + (8x – 15) = 360 \\
90 + 2x + 4 + 3x – 5 + 8x – 15 = 360 \\
13x + 74 = 360 \\
13x = 286 \\
x = 22
\]Answer: x = 22
ii. ∠B and ∠C
Step 1: Substitute the value of x in ∠B:
\[
\angle B = 2x + 4 \\
= 2(22) + 4 \\
= 48^\circ
\]Step 2: Substitute the value of x in ∠C:
\[
\angle C = 3x – 5 \\
= 3(22) – 5 \\
= 61^\circ
\]Answer: ∠B = 48° and ∠C = 61°



Leave a Comment