Introduction to Java: A Student-Friendly Guide
Imagine you want to tell your friend something — like “Let’s play football after school.” You use a common language like English or Hindi that both of you understand. But what if you wanted to talk to a computer or mobile phone?
Can you say “Let’s play football” to a computer and expect it to understand?
Of course not! Computers don’t understand human language. They only understand machine language or binary code.
What is Binary Code?
Binary code is the language of computers. It uses only two digits:0 and 1. So, instead of saying “Let’s play football,” a computer will see something like:
01001100 01100101 01110100 00100111 01110011 00100000 01110000…
Looks confusing, right? That’s why programming languages were created — to help humans communicate with computers in a more understandable way.
Programming Languages: Our Bridge to Computers
Programming languages like C, C++, Python and Java help us to command computers what to do. Programming Languages are easily understandable by the machine.
What is Pseudocode?
Before writing a program in any programming language, we often plan it out using pseudocode. Pseudocode means writing steps in English. For example:
- Step 1: Start
- Step 2: Ask the user for two numbers
- Step 3: Add the numbers
- Step 4: Show the result
- Step 5: End
Pseudocode helps you plan your logic without worrying about exact coding syntax.
What is a Flowchart?
A flowchart is a visual representation of a program or logic using shapes like arrows, rectangles, and diamonds. Some commonly used symbols are:
- 🟦 Rectangle = Process
- 🔷 Diamond = Decision
- 🟩 Oval = Start/End
It’s like drawing the path your program will take before actually coding it!
History of Java
Java was created by James Gosling and his team at Sun Microsystems in 1995.
It was first made for smart devices like TVs and set-top boxes but soon became popular on desktops, web and mobile platforms.In 2010, Oracle Corporation took over Java from Sun Microsystems.
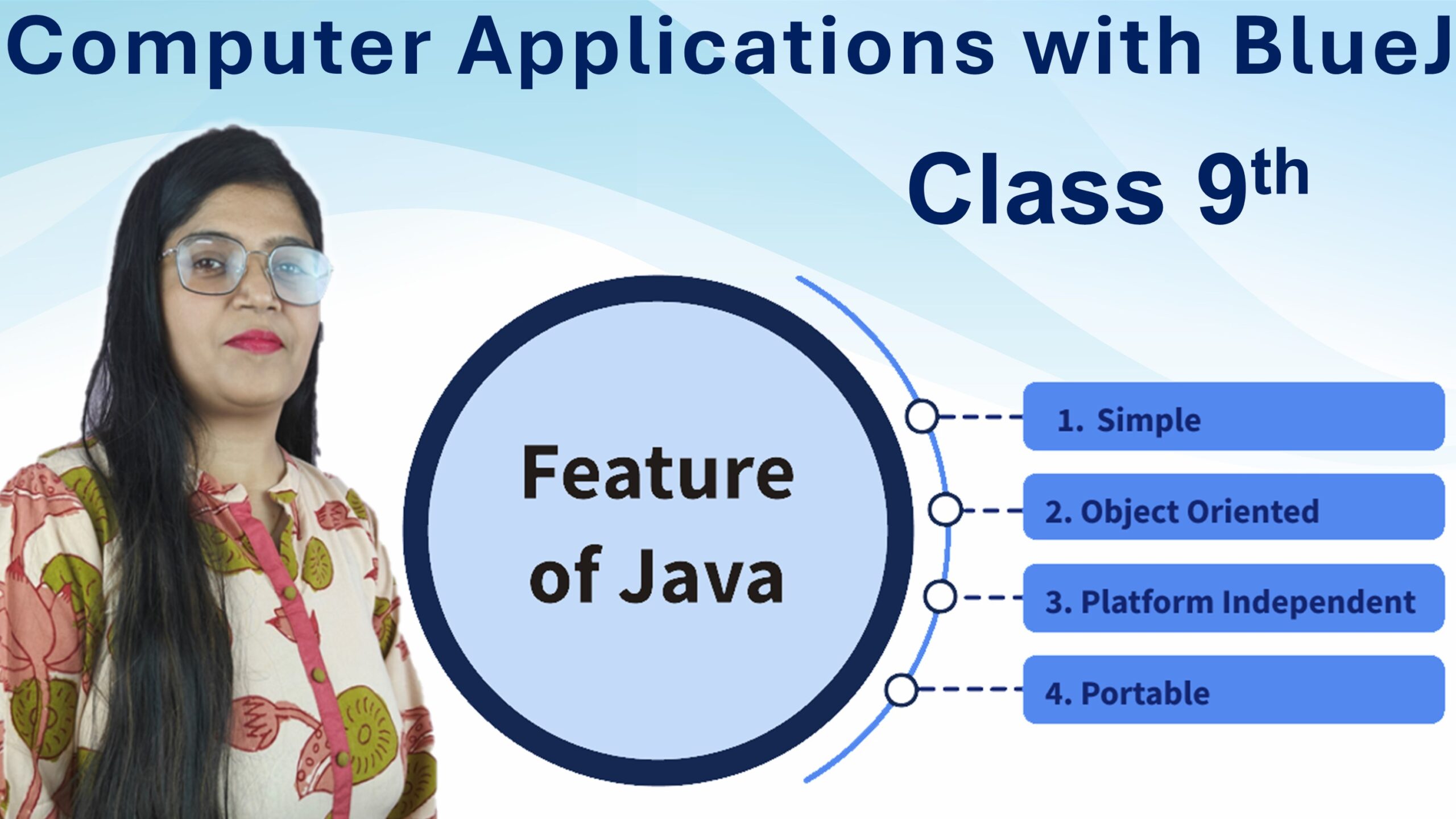
Features of Java
Here’s why Java is so powerful and popular:
- Simple – Easy to learn, especially if you know C or C++.
- Object-Oriented – Based on real-world objects and concepts.
- Platform Independent – “Write once, run anywhere” – Java works on any device.
- Secure – Used in banking and enterprise-level apps because of its safety features.
- Robust – Java can handle errors and crashes smoothly.
- Multithreaded – It can do multiple tasks at once (like loading a video while scrolling).
- Portable – Java programs can easily move from one system to another.
- Distributed – Java can build applications for the internet and networks.
Applications of Java
Java is used in:
- 🖥️ Desktop Applications – Tools like Eclipse, NetBeans
- 📱 Mobile Apps – Especially Android apps
- 🌐 Web Applications – Like banking systems, e-commerce
- 🏭 Enterprise Software – Business apps for large companies
- 🎮 Games and Simulation
- ☁️ Cloud Computing – Java is strong in cloud environments too
- 🧪 Scientific Applications
Companies That Use Java
Many top companies trust Java for their products:
- Google – Android apps
- Amazon – Backend systems
- Netflix – Video streaming platform
- Instagram – For server-side handling
- LinkedIn – Enterprise-level services
- Uber – Backend services
- Spotify – Music recommendation systems
- NASA – Simulation tools
Conclusion
Java is not just a programming language — it’s a tool to build amazing things in the digital world. From mobile games to banking apps, from web portals to smart devices — Java is everywhere.
If you’re thinking of learning programming, Java is a great place to start!



Leave a Comment