When a student first starts learning programming, the focus stays on writing code that works. But in real-world software development, writing code that others can understand matters even more. This is where Comments in Java play an important role.
Imagine reading a book with no punctuation or explanation. It becomes confusing very quickly. In the same way, code without comments becomes difficult to understand, maintain, and update.
That is why every Java developer, from beginners to professionals, uses comments regularly.
What are Comments in Java?
Comments in Java are non-executable lines in a program. The compiler ignores them completely. They exist only to help humans understand the code.
In simple words: Comments are notes written inside code to explain logic, purpose or instructions.
Why Comments Are Used in Java
Comments serve many important purposes:
- Improve Code Readability: They explain what the code is doing.
- Help During Debugging: Developers can temporarily disable code using comments.
- Support Team Collaboration: Other programmers can easily understand your logic.
- Document Code Logic: Complex formulas or algorithms become easier to understand.
Types of Comments in Java (With Syntax and Programs)
Understanding Comments in Java becomes easier when we study each type in detail with real examples. Java provides three main types of comments, and each serves a different purpose in writing clean and understandable code.
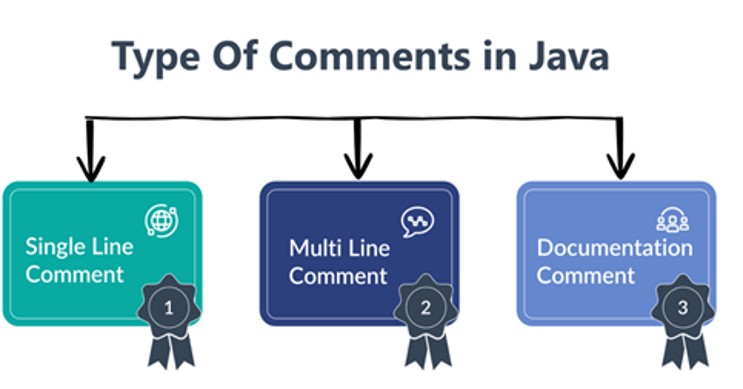
1. Single-Line Comments in Java
A single-line comment is used to write short explanations in one line. It begins with // and continues until the end of that line.
The Java compiler ignores everything written after //. This type is most commonly used by beginners and professionals because it is simple and quick.
Syntax:
// This is a single-line commentProgram:
public class SingleCommentExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declaring two integer variables
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 20;
// Calculating sum of numbers
int sum = num1 + num2;
// Displaying result
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
}
}Output:
Sum = 30When Should Single-Line Comments be used?
Use them when you want to:
- Explain a single statement
- Describe a variable
- Add a short note
- Temporarily disable one line of code
2. Multi-Line Comments in Java
A multi-line comment is used to write long explanations that may cover several lines. It starts with /* and ends with */. Everything written between these symbols is ignored by the compiler.
Syntax:
/* This is a
multi-line
comment */Program:
public class MultiCommentExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* This program demonstrates
how multi-line comments
are used to explain logic */
int length = 5;
int width = 4;
// Calculating area of rectangle
int area = length * width;
System.out.println("Area = " + area);
}
}Output:
Area = 20When Should You Use Multi-Line Comments?
- Explain complex logic
- Describe algorithms
- Write large notes
- Comment out multiple lines of code
3. Documentation Comments (Javadoc Comments)
A documentation comment is a special type of comment used to generate official documentation for Java programs. It starts with /** and ends with */.
These comments are processed using the Javadoc tool, which creates HTML documentation automatically. This type is widely used in professional software development.
Syntax:
/**
* Documentation comment
*/Program:
/**
* This class demonstrates
* the use of Javadoc comments.
*/
public class JavadocExample {
/**
* This method prints a welcome message.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java Comments");
}
}Output:
Welcome to Java CommentsWhen Should You Use Multi-Line Comments?
- Explain complex logic
- Describe algorithms
- Write large notes
- Comment out multiple lines of code
Comparison of All Types of Comments in Java
| Feature | Single-Line | Multi-Line | Documentation |
| Symbol | // | /* */ | /** */ |
| Length | One line | Multiple lines | Multiple lines |
| Purpose | Quick notes | Detailed explanations | Official documentation |
| Used By | Beginners & developers | Developers | Professional programmers |
| Documentation Tool | No | No | Yes (Javadoc) |
Benefits of Comments in Java
Understanding the benefits of Comments in Java is very important for students as well as professional developers. Comments do not affect program execution, but they greatly improve the quality of code.
In real-world software development, writing code without comments is considered a bad practice. Good commenting makes programs easier to understand, maintain, and update.
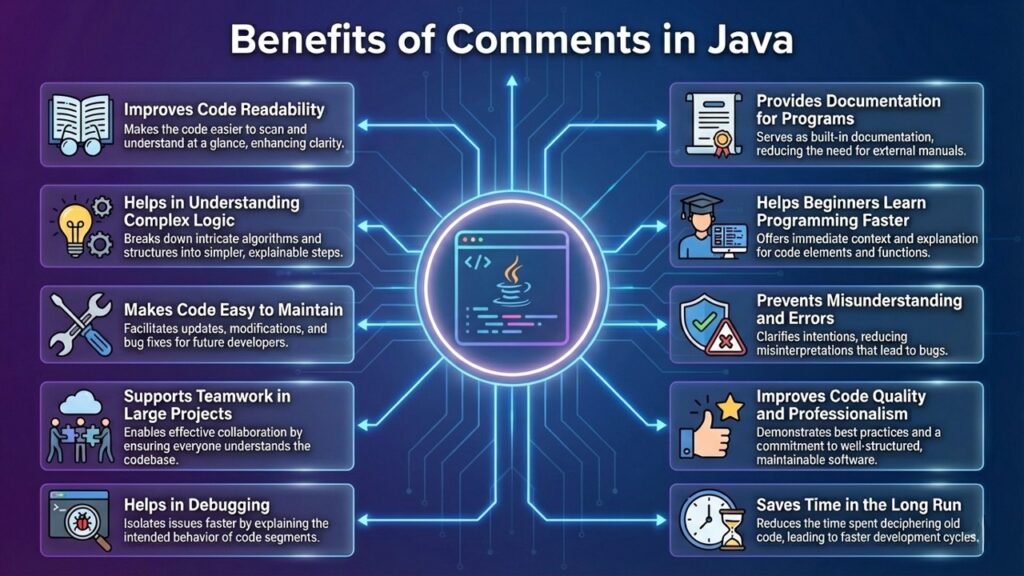
Let us study each benefit in detail.
- Improves Code Readability: The biggest advantage of Comments in Java is that they make code easy to read. When someone reads a program, they may not understand the logic immediately. Comments explain what the code is doing in simple language.
- Helps in Understanding Complex Logic: Some programs contain complicated calculations or algorithms. Without comments, such code becomes very difficult to understand.
- Makes Code Easy to Maintain: Software projects are updated frequently. Sometimes the same code is modified after months or years. Without comments, developers may forget the original logic.
- Supports Teamwork in Large Projects: Most real-world Java applications are developed by teams, not by a single person. In such situations, comments act like communication between developers.
- Helps in Debugging: Debugging means finding and fixing errors in a program. Comments help debugging in two ways:
- a) Explaining Logic: Developers can quickly understand which part of code might be causing the error.
- b) Temporarily Disabling Code: You can comment out code to test specific sections.
- Provides Documentation for Programs: Documentation comments (Javadoc) help generate official program documentation. This documentation explains:
- Class purpose
- Method usage
- Input parameters
- Output details
- Helps Beginners Learn Programming Faster: For students, comments act like a teacher inside the code. They explain:
- What each line does
- Why a method is used
- How a program works step by step
- Prevents Misunderstanding and Errors: Without comments, developers may misunderstand code logic. This can lead to:
- Wrong updates
- Incorrect bug fixes
- Program failures
- Clear comments reduce such risks.
- Improves Code Quality and Professionalism: Well-commented code looks clean, organized and professional. Companies prefer developers who follow proper commenting practices because it shows:
- Good coding habits
- Clear thinking
- Responsibility
- Saves Time in the Long Run: Writing comments may take extra time initially, but it saves a lot of time later when:
- Reviewing code
- Fixing errors
- Updating programs
- Sharing projects
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Conclusion
All three types of Comments in Java help developers write understandable, maintainable and professional code. Choosing the right type depends on how much explanation you need and the purpose of your program.
If you’re thinking of learning programming, Java is a great place to start!




Leave a Comment